End to End Configuration of AR in R12
There are few key steps that are to be configured outside of AR
1. Define Ledger with LE
2. Define Operating Unit and link to Ledger and LE
3. Define atleast one Inventory Item Organization
4. Define Item Validation Organization in Order Management – We can share this menu, if we don’t implement OM
5. Define Tax in EB Tax.
6. Define banks, branches and accounts – Possible to configure through AR, if security is enabled through UMX security wizard
7. Define or Assign key profile option values to AR responsibilities
Define all the following setup using Receivables Manager responsibility:
Define System Option
Define system options to customize your Receivables environment. During Receivables setup, you specify your accounts, customer and invoice parameters, and how the Auto Invoice and Automatic Receipts programs will run.
Setup>System>System Option
Define system option for each Operating Unit.
Define Payment Terms
Receivables lets you define standard payment terms for your customers to specify the due date and discount date for their open items. Payment terms can include a discount percent for early payment and you can assign multiple discounts to each payment term line. For example, the payment term '2% 10, Net 30' indicates that a customer is allowed a two percent discount if payment is received within 10 days; after 10 days, the entire balance is due within 30 days of the transaction date with no applicable discount.
Setup>Transaction>Payment Term
Define Transaction Type
Use transaction types to define the accounting for the debit memos, credit memos, on-account credits, chargebacks, commitments, invoices, and bills receivable you create in Receivables. Transaction types also determine whether your transaction entries update your customers' balances and whether Receivables posts these transactions to your general ledger.
Setup>Transaction>Transaction Type
Define this for each operating unit. Define transaction type for atleast Invoi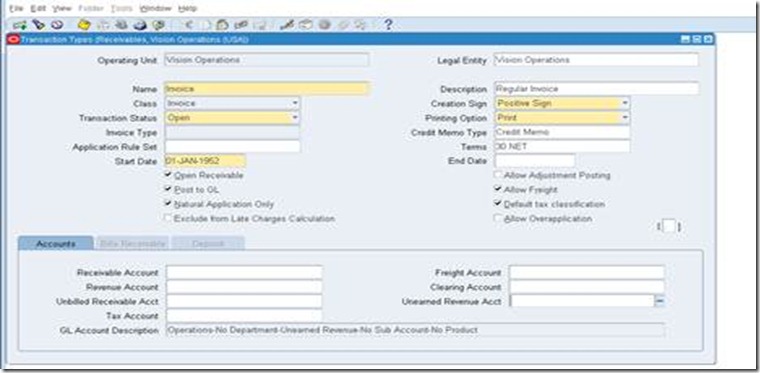
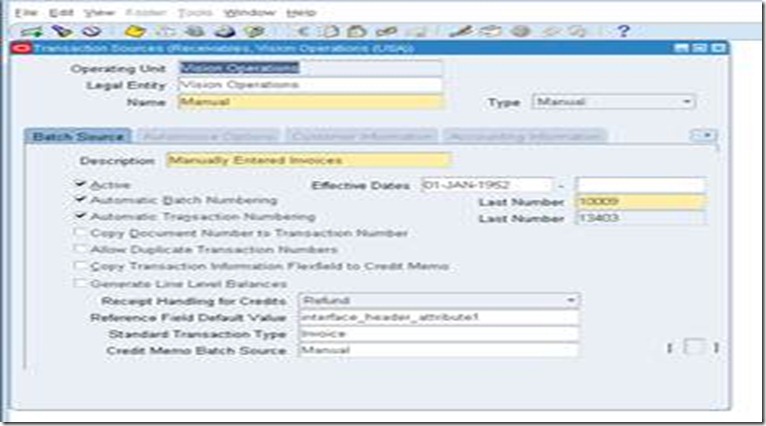
Define Transaction Source
Batch sources control the standard transaction type assigned to a transaction and determine whether Receivables automatically numbers your transactions and transaction batches. Active transaction batch sources appear as list of values choices in the Transactions, Transactions Summary, and Credit Transactions windows, and for bills receivable in the Bills Receivable and Bills Receivable Transaction Batches windows.
Setup>Transaction>Source
Define this for each operating unit. Select Type as ‘Imported’, if invoice is to be imported into AR from third party/legacy/external systems.
Define Memo Lines
Standard memo lines are lines that you assign to a transaction when the item is not an inventory item (for example, 'Consulting Services'). You can assign memo lines to debit memos, on-account credits, debit memo reversals, chargebacks, commitments, and invoices. Receivables display your standard memo lines as list of values choices during credit memo entry in the Credit Transactions window and during invoice entry in the Lines window. When you create chargebacks and debit memo reversals, you can either use the standard line that Receivables provides or enter your own. You can create an unlimited number of standard memo lines.
Setup>Transaction>Memo Lines
Define this for each operating unit. This is particularly important, if we implement AGIS.
Define Accounting Rules
Define accounting rules to create revenue recognition schedules for your invoices. Accounting rules determine the number of periods and percentage of total revenue to record in each accounting period. You can use accounting rules with transactions that you import into Receivables using Auto Invoice and with invoices that you create manually in the Transaction windows. You can define an unlimited number of accounting rules.
This is generally applicable to project based invoices, property invoices etc.
Setup>Transaction>Accounting Rules
Define Auto Accounting
Define Auto Accounting to specify how you want Receivables to determine the default general ledger accounts for transactions that you enter manually or import using Auto Invoice. Receivables creates default accounts for revenue, receivable, freight, tax, unearned revenue, unbilled receivable, late charges, bills receivables accounts, and Auto Invoice clearing (suspense) accounts using this information.
Setup>Transaction>Auto Accounting
Define this for each operating Unit. Define this atleast for revenue, receivable, freight, tax, unearned revenue, unbilled receivable, bills receivables accounts, and Auto Invoice clearing.
Tax code will default from EB Tax, which can be updated/modified here in this auto accounting window.
Define Approval Limit
Use the Approval Limits window to define approval limits for Adjustments, Receipt Written off, Credit memo refund and Credit memo
Setup>Transaction>Approval Limit
Define this for each user.
Define Receivables Activities
Define receivables activities to default accounting information for certain activities, such as miscellaneous cash, discounts, late charges, adjustments, and receipt write-off applications.
Setup>Receipts>Receivables Activities
Define this for each operating unit. This can be configured only after EB Tax configuration.
Define Auto Cash Rule set - Optional configuration
Define Auto Cash Rule Sets to determine the sequence of Auto Cash Rules that Post Quick Cash uses to update your customer's account balances. You specify the sequence and the Auto Cash Rules for each Auto Cash Rule Set. The Auto Cash Rule Sets you define display as list of values choices in the Customers, Customer Addresses, Customer Profile Classes, and the System Options windows. Post Quick Cash first checks the customer site, then the customer profile class, and finally at the system options level to determine the Auto Cash Rule Set to use.
Setup>Receipts>Auto Cash Rule Set
Define Application Rule Set – We can use seeded configuration
Use the Application Rules Sets window to review existing and define new application rule sets. Application rule sets specify the default payment steps for your receipt applications and how discounts affect the open balance for each type of associated charges. By defining your own application rule set, you can determine how Receivables reduces the balance due for a transaction's line, tax, freight, and late charges.
Setup>Receipt>Application Rule Set
Define Receipt Classes
Define receipt classes to determine the required processing steps for receipts to which you assign receipt methods with this class. These steps include confirmation, remittance, and reconciliation. You can specify any combination of these processing steps with one exception: if you confirm and reconcile, then you must also remit. If you enter No for all three of these steps, Receivables automatically creates receipts assigned to this receipt class with a status of Cleared.
Setup>Receipt>Receipt Classes
Define this for each operating unit. Only header window is not OU based but bank accounts window are OU specific.
This requires some experience to use this configuration. Basic configuration is simple but it is key configuration to handle various receipts like Credit Card integration, Auto lock box, Bill of Exchange, and Factoring. This requires very good practice and knowledge on Function Capturing Process as well.
Define Receipt Sources
Define receipt batch sources to provide default values for the receipt class, receipt method, and remittance bank account fields for receipts you add to a receipt batch. You can accept these default values or enter new ones. Receipt batch sources can use either automatic or manual batch numbering.
Setup>Receipt>Receipt Sources
Define this for each operating unit. This is for grouping of receipt class, payment method and bank account.
Define Collector
Receivables let you define collectors and assign them to a profile class, or directly to a customer account or site. When you assign a collector to a profile class, that collector becomes the collector for all customers assigned that profile class. You can modify collector assignments for your customers in the Customers pages, and for your profile classes in the Customer Profile Classes window.
Setup>Collections>Collector
Employee needs to be configured and Collector setup is to be done in CRM.
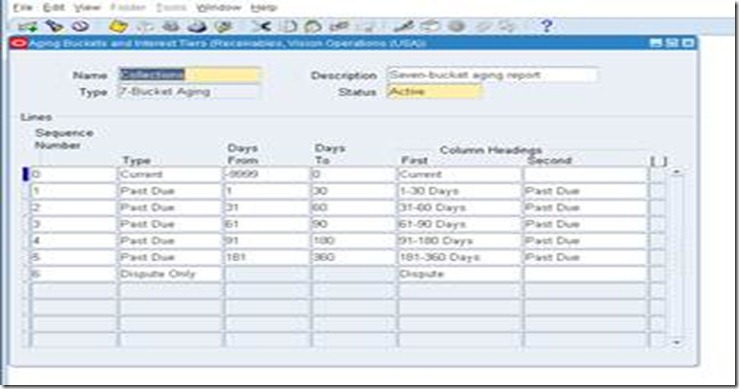
Define Aging bucket
Aging buckets are time periods you can use to review and report on your open receivables. For example, the 4-Bucket Aging bucket that Receivables provides consists of four periods: -999 to 0 days current, 1 to 30 days past due, 31-61 days past due, and 61-91 days past due. When you create your Collections reports, you can specify an aging bucket and 'as of date', and Receivables will group the transactions and their amounts in the appropriate days past due period.
Setup>Collection>Aging Buckets and Interest Tiers
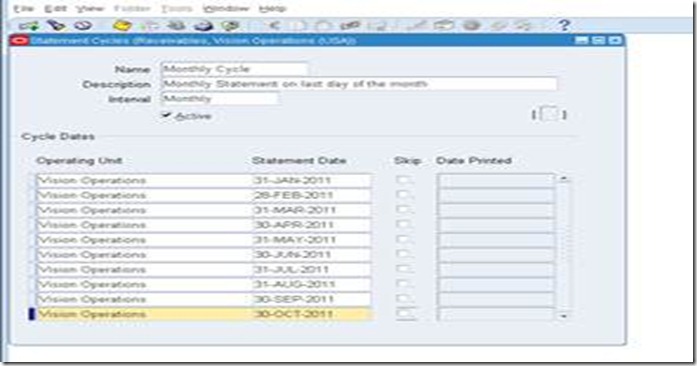
Define Statement Cycles
Define statement cycles to determine when to send statements to your customers. You enter statement cycles when you define or modify individual customer and site profile classes in the Customer Profile Classes window.
Setup>Print>Statement Cycles
Define this for each operating unit. Customer statement will use this cycle.
Define standard message – Optional
Define standard messages to provide the text that Receivables prints on the bottom of your customer's statements, debit memos, and interest invoices. You can use messages to inform your customers of special promotions or to make your printed documents more personal.
Setup>Print>Standard message
This message can be used in Customer Statement.
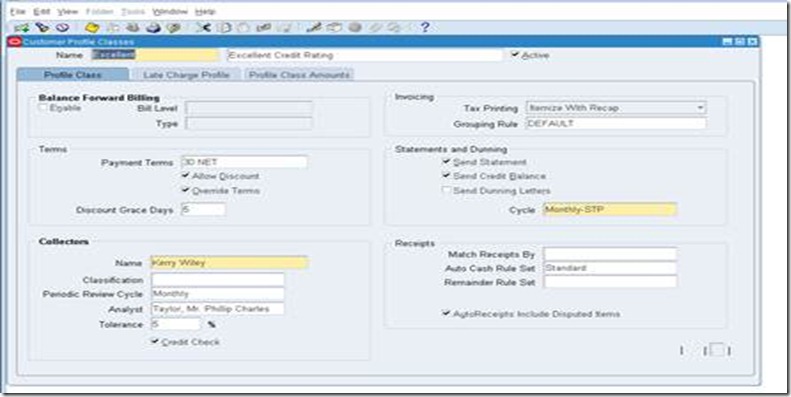
Define Profile Class
Use Customer Profiles to group customer accounts with similar creditworthiness, business volume, payment cycles, and late charge policies. For each profile class you can define information such as credit limits, payment terms, statement cycles, invoicing, and discount information. You can also define amount limits for your late charges and statements for each currency in which you do business.
Customers>Profile Classes
This is important for consolidated billing, late charges, profile class based strategy in collections and very important configuration for business in real time.
Define Customers – Initially customers will be migrated from external/legacy/older version of Oracle EBS.
Define Remit to address
Setup>Print>Remit to address
Open or Close AR accounting period
Open and close accounting periods in your calendar to control the recording of accounting information for these periods. Receivables lets you open future accounting periods while your current period is still open. Receivables also lets you reopen previously closed accounting periods and enter receivables activities without transferring transactions to the general ledger when you set your accounting periods to 'Future.'
Control>Accounting>Open or Close periods
**** This is ledger based. Open / Close the period in one OU will Open / Close the period in another OU as long as bot the OU shares the same Ledger.















4 comments:
Great effort.Thnx for ur help
Thanx for your help
Great effort.
Thank you for posting this. Very elaborate and helpful
- Prasenjeet
Good effort Sir.Useful Post.
-
Honey Khandelwal.
Post a Comment